Hey there!,
In this post, we will explore how to integrate Elastic Alert with IRIS using Tines. First let’s introduce IRIS V2:
What is IRIS V2?
IRIS V2 is an open-source incident response platform designed to help cybersecurity teams collaborate and manage investigations effectively. It allows users to process alerts, manage cases, track evidence, and automate tasks. IRIS supports integration with various tools (like VirusTotal and MISP), has an API for automation, and is easy to deploy via Docker. The platform, created by the Airbus Cybersecurity CSIRT team, is highly customizable and aims to streamline incident response operations for organizations.
To successfully implement the integration of Elastic Alert Tracking with IRIS V2 using Tines, we can break down the process into a set of structured steps, as follows:
Prerequisites
- Elasticsearch instance: Ensure Elasticsearch is running in your environment.
- IRIS V2 ticketing system: IRIS V2 must be hosted and accessible for the ticketing integration.
- Tines SOAR platform: Tines must be accessible from your environment.
- ngrok: You can use ngrok platform to expose Elasticsearch and IRIS V2 to Internet.
High-Level Overview
- Deploy IRIS V2.
- Connect Elasticsearch with Tines via the Elasticsearch API.
- Configure Tines to automate the alert retrieval from Elasticsearch and integrate ticket creation into IRIS V2.
Step 1: IRIS V2 Installation and Configuration
- IRIS V2 Overview:
- IRIS V2 is an open-source incident response and ticketing platform designed for handling security events. It offers collaborative workflows and structured investigations.
- Visit the official IRIS documentation for guidance on installation, or use their GitHub repository to download the latest release.
- Installation Steps:
- Pre-requisites: You will need a system configured with Docker and Docker Compose (IRIS runs as Docker containers).
- Install Docker:
##### Install necessary prerequisites: sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software properties-common ##### Add Docker’s official GPG key: curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg ##### Set up the stable Docker repository: echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null ##### Update your package list to include Docker’s repository: sudo apt update ##### Install Docker: sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
- Install IRIS V2:
- Clone the IRIS repository:
git clone https://github.com/dfir-iris/iris-web.git cd iris-web

- Environment configuration:
Customize the
.envfile to set up credentials, database connections, and other necessary configurations.

- Clone the IRIS repository:
- Start IRIS V2:
- Use Docker Compose to start the service:
docker-compose up
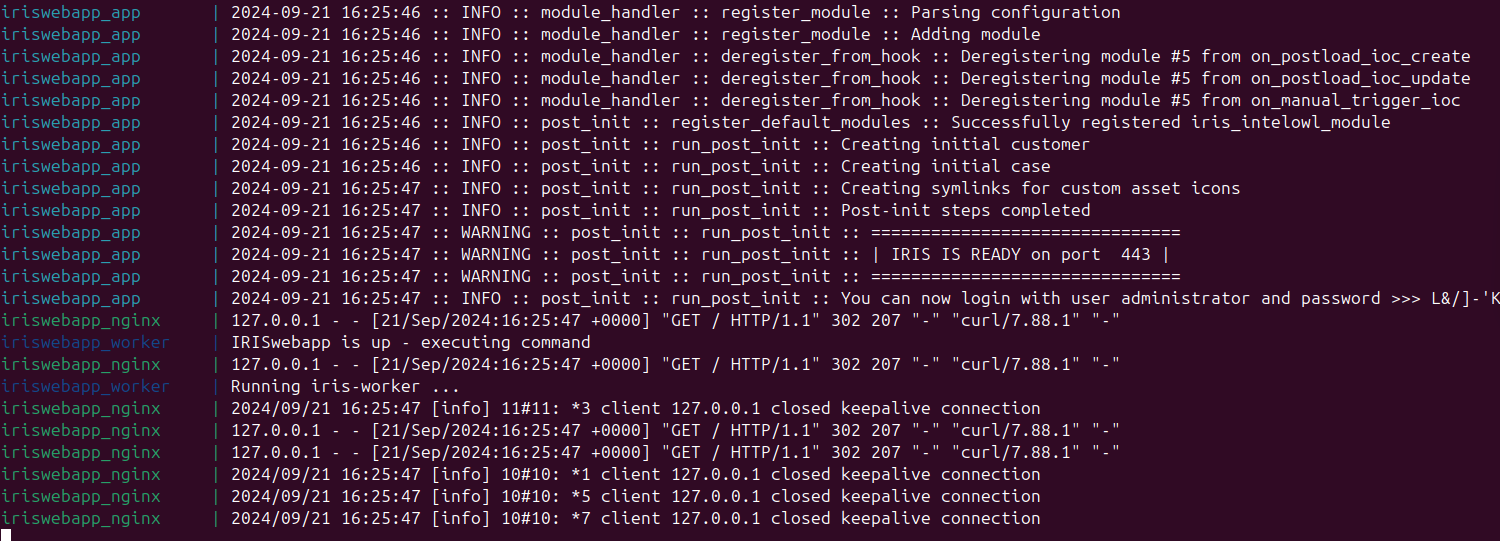
 Check logs to get administrator’s password:
Check logs to get administrator’s password:
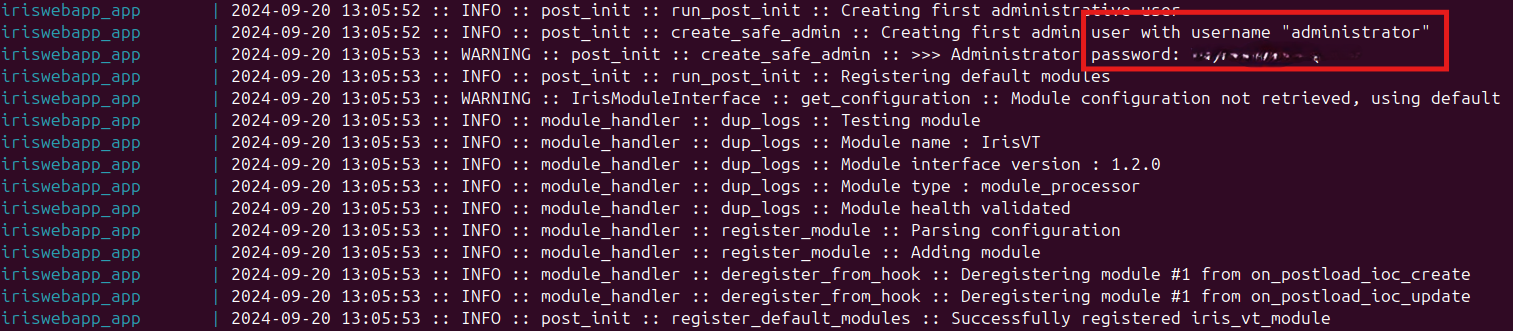 After installation, IRIS V2 should be accessible via a web browser at the configured IP and port.
After installation, IRIS V2 should be accessible via a web browser at the configured IP and port.


- Use Docker Compose to start the service:
Use ngrok to expose the local IRIS V2 and Elasticsearch service to the internet:
Ngrok is a tool that provides secure tunnels to expose a local server or service to the internet. It enables us to share our local environment with external users without deploying to a cloud server.
Install ngrok via Apt:
curl -sSL https://ngrok-agent.s3.amazonaws.com/ngrok.asc | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/ngrok.asc >/dev/null && echo "deb https://ngrok-agent.s3.amazonaws.com buster main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ngrok.list && sudo apt update && sudo apt install ngrok
Create account on https://ngrok.com and navigate to Your Authtoken
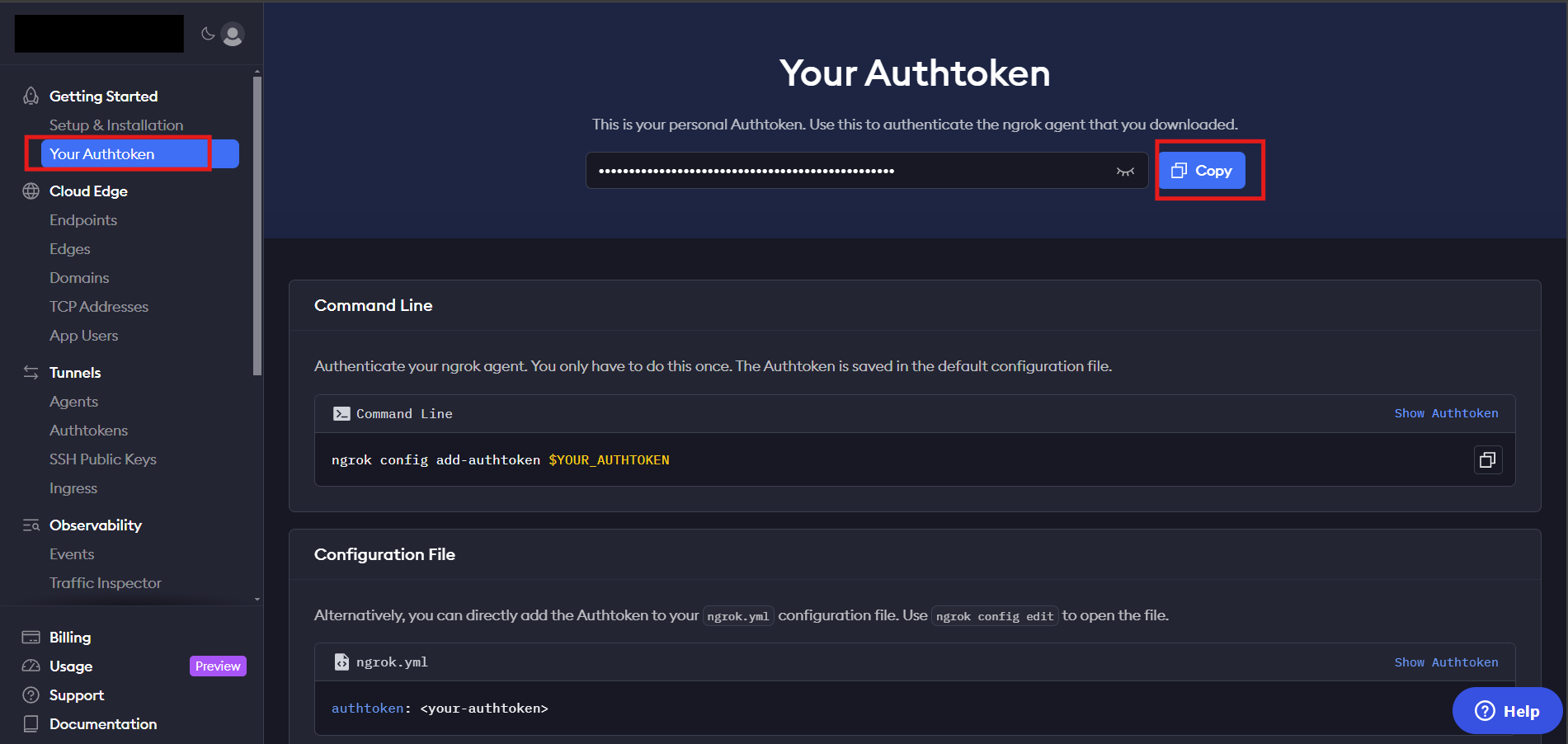 Add authtoken:
copy you
Add authtoken:
copy you Authtoken and run: ngrok config add-authtoken <token>
- Edit
ngrok.yml: Run
Run ngrok start --allto startngrok: Check Elasticsearch:
Check Elasticsearch:

 Check IRIS:
Check IRIS:

Step 2: Elasticsearch Integration Using Tines
- Tines Overview:
- Tines is a Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platform that can automate workflows by interacting with different APIs.
Add Alerts to Elasticsearch
- Index a set of simulated alerts into Elasticsearch.
- Use the Bulk API to upload alerts in JSON format for later retrieval via Tines.
- Example JSON structure:
- Tines is a Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platform that can automate workflows by interacting with different APIs.
{ "index": { "_index": "alerts" } }
{ "timestamp": "2024-09-20T12:00:00", "alert_id": "1", "alert_type": "security", "message": "Unauthorized login attempt detected", "severity": "high", "status": "active" }
{ "index": { "_index": "alerts" } }
{ "timestamp": "2024-09-20T12:15:00", "alert_id": "2", "alert_type": "performance", "message": "CPU usage exceeded 90%", "severity": "medium", "status": "active" }
{ "index": { "_index": "alerts" } }
{ "timestamp": "2024-09-20T12:30:00", "alert_id": "3", "alert_type": "security", "message": "Multiple failed login attempts detected", "severity": "critical", "status": "active" }
{ "index": { "_index": "alerts" } }
{ "timestamp": "2024-09-20T13:00:00", "alert_id": "4", "alert_type": "performance", "message": "Memory usage exceeded 80%", "severity": "medium", "status": "resolved" }
{ "index": { "_index": "alerts" } }
{ "timestamp": "2024-09-20T13:30:00", "alert_id": "5", "alert_type": "security", "message": "Potential SQL injection detected", "severity": "high", "status": "active" }
Check on Kibana: Stack Management -> Index Management

- Retrieve Elasticsearch Alerts:
- API Access to Elasticsearch:
Elasticsearch provides a RESTful API to query SIEM alerts. You will need to configure an appropriate query to retrieve these alerts.
Example query to get alerts from an Elasticsearch instance:
POST /alerts/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} } }
- API Access to Elasticsearch:
Elasticsearch provides a RESTful API to query SIEM alerts. You will need to configure an appropriate query to retrieve these alerts.
Example query to get alerts from an Elasticsearch instance:
Ensure the API is reachable and correctly configured for access via Tines.
- Configure Tines Story for Elasticsearch Alert Retrieval:
- Create an Agent in Tines that retrieves alerts from Elasticsearch.
- Use the HTTP Request Action in Tines to send a POST request to Elasticsearch API.
- Configure the request parameters, including Elasticsearch credentials, endpoint, and query body.
- Example Tines action configuration:
- Create an Agent in Tines that retrieves alerts from Elasticsearch.
{
"url": "https://e6b6-105-3.ngrok-free.app/alerts/_search",
"content_type": "json",
"method": "post",
"payload": {
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"unique_alerts": {
"terms": {
"field": "alert_id.keyword",
"size": 10
},
"aggs": {
"top_alerts_hits": {
"top_hits": {
"size": 1,
"_source": {
"includes": [
"alert_id",
"alert_type",
"message",
"severity",
"timestamp",
"status"
]
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
"basic_auth": [
"elastic",
"yourpasswd"
]
}
Explanation of the Example:
-
Size of Hits:
The"size": 0is set to prevent Elasticsearch from returning the default search results. Since we are interested in unique alerts, we only want the aggregated results. -
Aggregation:
Theaggsfield introduces a terms aggregation on thealert_id.keywordfield. This will group all alerts by their uniquealert_id. -
Top Hits Aggregation:
Thetop_hitsaggregation under each unique bucket ensures that only the latest entry for each uniquealert_idis returned, with fields likealert_id,alert_type,message,severity,timestamp, andstatus. -
Field Name:
I’ve usedalert_id.keywordbecause Elasticsearch stores terms aggregations on exact (not analyzed) values, which often requires using the.keywordversion of the field (depending on your mapping).
Test:
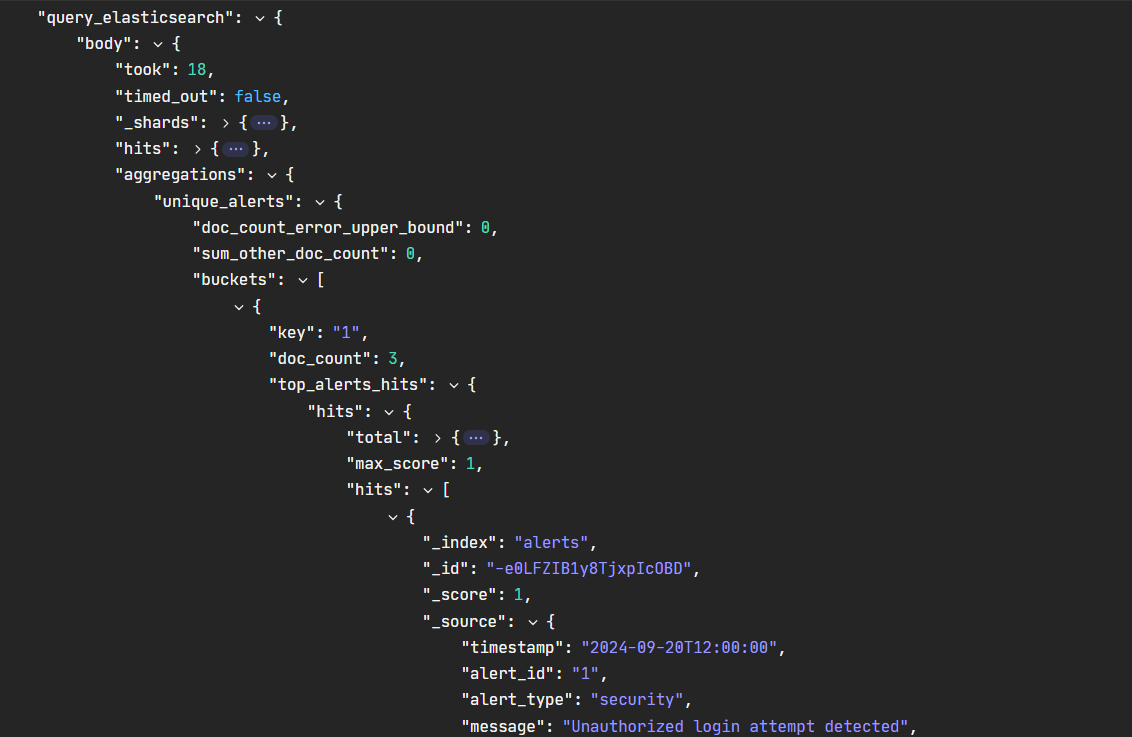
Transform the data retrieved from the Elasticsearch query by adding Event Transform:

Set Mode to “Explode”, which means that the data will be broken down into individual events. It creates multiple events from a single object (useful for iterating through arrays or lists).

The path is query_elasticsearch.body.aggregations.unique_alerts.buckets, which means that this path points to a specific part of that response where we need to extract the data.
To: The result of the transformation is being sent to the field alert_title, which stores the alert titles found in the Elasticsearch query.
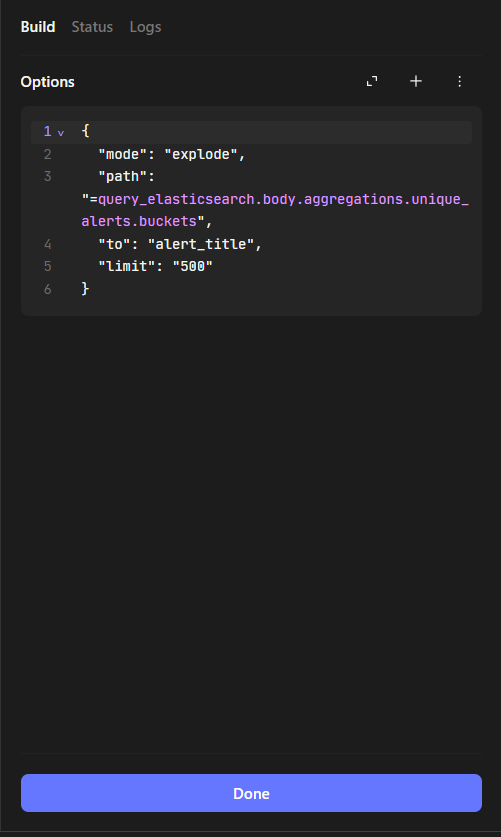
Add another Event Transform:
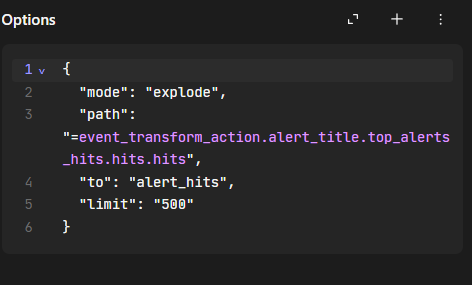
Set path to drill down into the alert data’s nested structure to extract individual “hits”
Each item (or “hit”) from the exploded array will be stored or processed under the alert_hits field.
Step 3: Alert Ticketing in IRIS V2
- IRIS V2 Ticket Creation via API:
- IRIS provides a REST API for ticket creation. Use this API in conjunction with the data retrieved from Elasticsearch via Tines.
- Example API call to create a ticket:
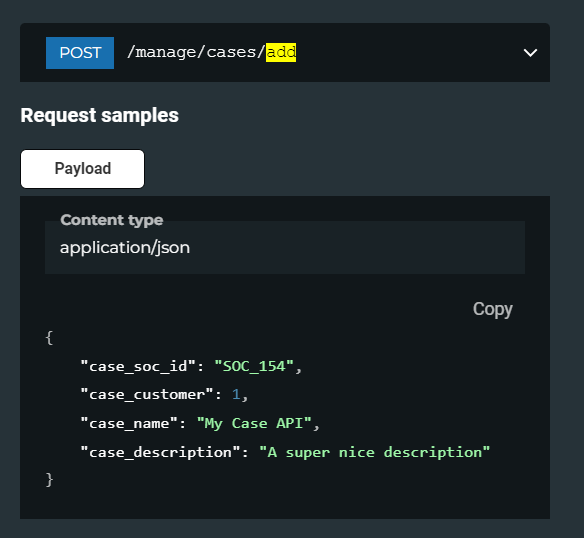

- Configure Tines Story for Ticket Creation:
- Create another agent in Tines that handles IRIS ticket creation.
- This agent should listen for new data (Elasticsearch alerts) from the previous agent and then create tickets in IRIS using the HTTP Request Action.
- Example configuration:
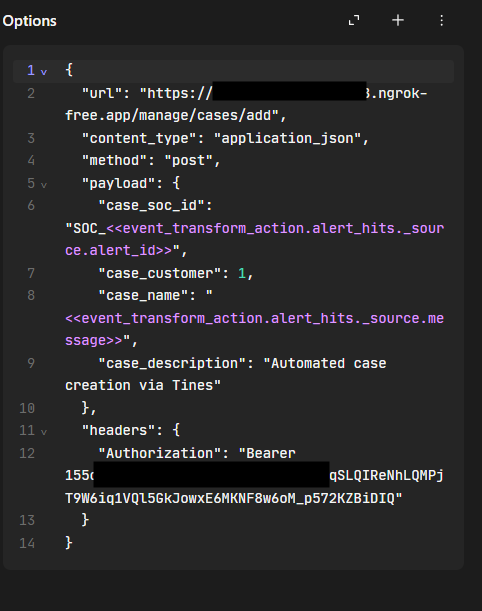

- Create another agent in Tines that handles IRIS ticket creation.
- URL: Sends a
POSTrequest to the IRIS V2 API (exposed via ngrok). - Payload: Contains case details, including the SOC alert ID and message extracted from the alert (
alert_id,message). - Authorization: Uses a Bearer token for API authentication.
To obtain an API key. Each user is automatically attributed one when it is created. It can be found on the left panel, under username and
My Settings.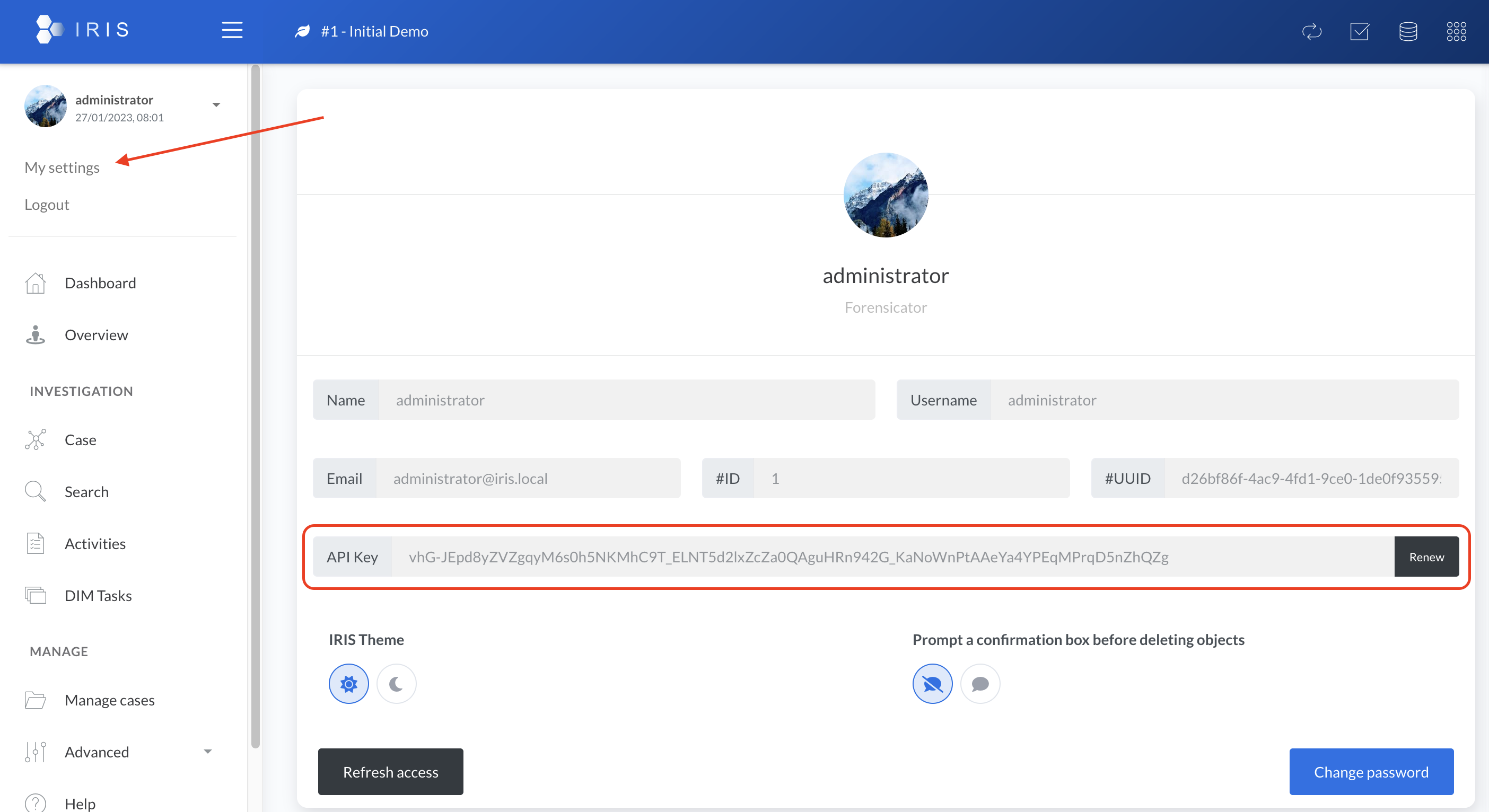
Step 4: Testing and Evaluation
-
Run the Full Workflow:
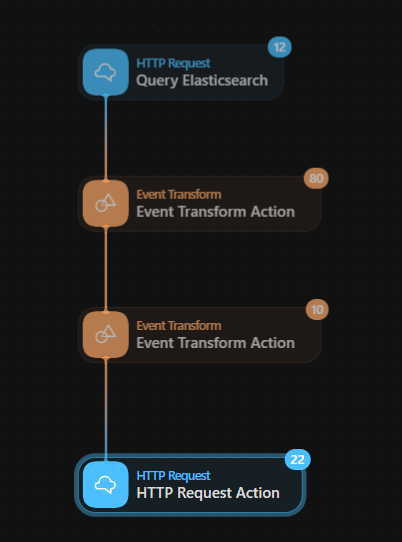
- Ensure that alerts are being pulled from Elasticsearch by checking the logs and monitoring activity in Tines.
- Confirm that for every alert retrieved by Tines, a corresponding ticket is created in IRIS V2. Cross-check the alert details with the tickets.
-
Validate System Operation:

By following these steps, you’ll have a robust system that integrates Elasticsearch SIEM alerts with the IRIS V2 ticketing system, managed via Tines.
