Rule#1: Detecting Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks with Snort
Understanding the Attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack overwhelms a target by sending a flood of packets, making it unavailable for legitimate users. The Snort rule for detecting a Ping Flood (a form of DoS attack using ICMP packets) monitors the network for excessive ICMP traffic, which is typically used by ping utilities. Send flood ping packets using “ping -f”
Generating the Ping Flood
To test this rule, a flood of ICMP ping packets is generated using the following command:
ping -f <target IP>
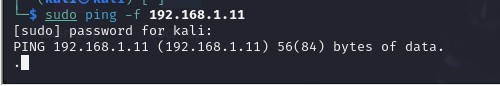
This command sends multiple ICMP echo requests (pings) to a specific IP address rapidly.
Snort Rule for Ping Flood Detection
The Snort rule to detect this ping flood is written as follows:
Rule:
alert icmp any any -> any any (msg:"Ping Flood detected"; threshold:type both, track by_src, count 100, seconds 1; sid:1000004; rev:1;)
Monitoring and Response
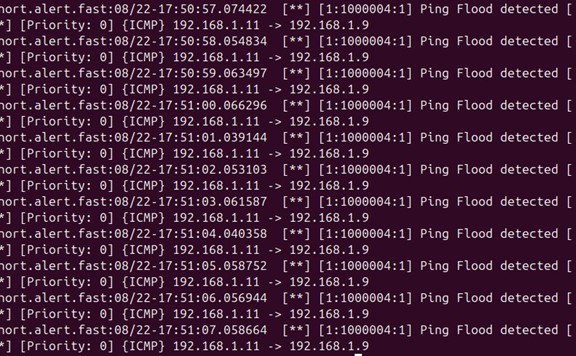
Once the Snort rule is applied and snort is running the system will alert when it detects a ping flood. The threshold is set to track by source IP and count 100 packets in 1 second. This means that if the system detects 100 ICMP packets from the same source IP in 1 second, it will trigger an alert.
Rule#2: Unencrypted Login Credentials Detection
Vulnerability Identification
Many login forms on websites transmit sensitive user credentials (like usernames and passwords) without encryption, especially over HTTP (port 80). This is a major security risk, as attackers can easily capture these credentials through packet sniffing tools like Wireshark.
Setting Up a Test Scenario
To simulate an unencrypted login detection scenario, a simple HTML login form is hosted on an Apache server. The Apache server listens on port 80 (the default HTTP port) and delivers the login form to users. The form is designed to send the username and password to the server without encryption.
Create a Sample Login Page, and host the “index.html” file on Apache server.
💡 You can head to this post Here to know how to setup an apache server.
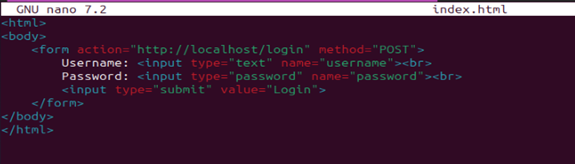
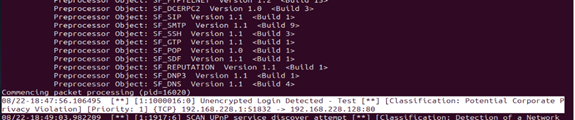
The following Snort rule is designed to detect any login attempts over unencrypted channels:
Rule:
alert tcp any any -> any 80 (msg:"Unencrypted Login Detected - Test"; content:"password="; sid:1000016; classtype:poli>
Testing and Response
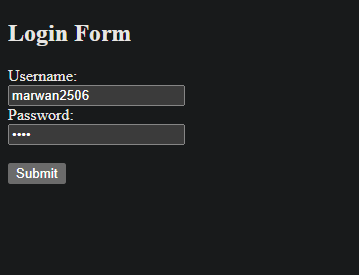
The test is carried out by submitting login credentials through the unencrypted form. Snort will trigger an alert as soon as it detects a POST request on port 80.
Rule#3: Detecting Traffic from an Outer Country
Understanding the Need
In many cases, traffic originating from specific countries may be considered suspicious due to high rates of cyber-attacks. Network administrators might want to block or monitor traffic from certain geographic regions.
Setting Up the VPN
To test this rule, the network administrator sets up a VPN on a Windows machine to simulate traffic originating from a foreign country. The VPN is configured to use a server located in a different country.
Open a VPN on the windows machine and access the Apache Server

The Snort rule to detect traffic from a list of blocked foreign IP ranges is as follows:
Rule:
alert tcp ![41.0.0.0/8,156.0.0.0/12,197.0.0.0/8] any -> $HOME_NET 80 (msg:"Alert: HTTP Request from Outside Egypt"; flow:to_server,established; content:"GET "; http_method; sid:1000025; classtype:policy-violation;)
Monitoring and Response
Once the rule is in place, any TCP traffic that originates from IP ranges not included in the specified list will trigger an alert. This helps network administrators to block unwanted or suspicious traffic from external sources.

